What is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
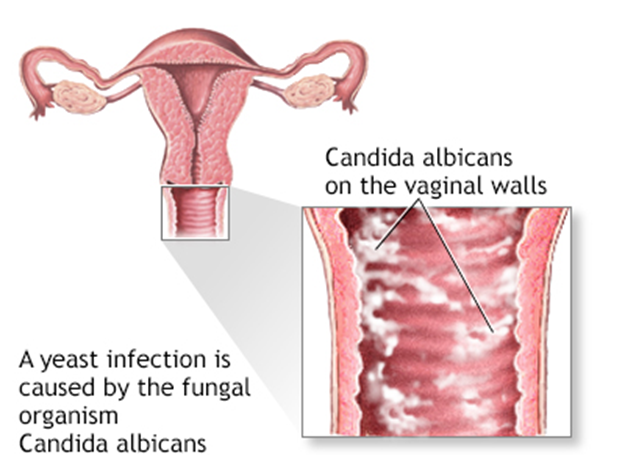
A vaginal yeast infection occurs when the balance of microorganisms in the vagina is disrupted, allowing Candida to overgrow. This imbalance can result from several factors, including changes in the body’s hormonal levels, use of antibiotics, and changes in lifestyle. The infection typically leads to inflammation and irritation, which can be uncomfortable and disruptive to a woman’s daily life.
Causes of Vaginal Yeast Infections
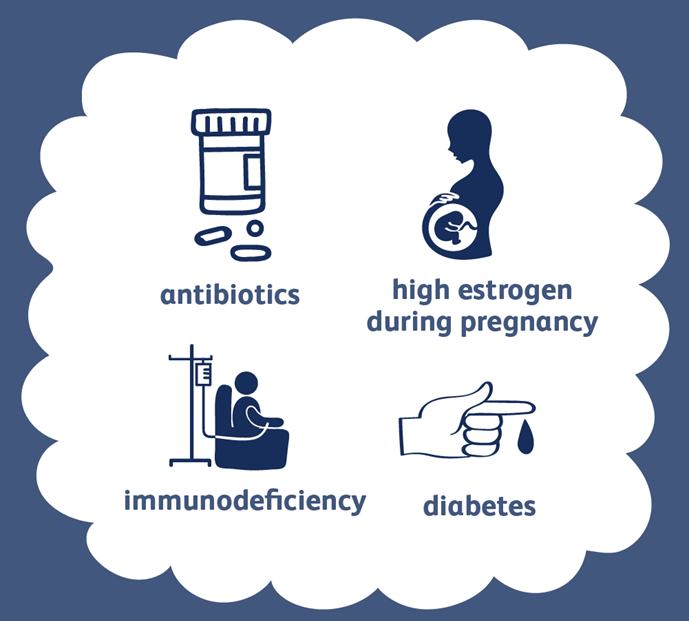
Yeast infections are most commonly caused by Candida albicans , but other species of Candida can also contribute to the infection. Several factors can trigger an overgrowth of Candida in the vagina, including:
1.Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics, while effective in treating bacterial infections, can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina. This disruption often leads to an overgrowth of yeast. Since antibiotics target both harmful bacteria and beneficial bacteria, the reduction in beneficial bacteria allows yeast to proliferate.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can alter the environment of the vagina, making it more susceptible to yeast infections. For example, during pregnancy, increased estrogen levels can encourage yeast growth.
3. Uncontrolled Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can promote the growth of yeast, as Candida thrives in sugar-rich environments. Women with poorly controlled diabetes are at a higher risk for developing yeast infections.
4. Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system, due to conditions like HIV or the use of immunosuppressive medications, can make it more difficult for the body to control the growth of Candida , leading to infections.
5. Excess Moisture or Warmth
Wearing tight-fitting clothing, synthetic underwear, or damp clothing for extended periods (such as after swimming or exercise) can create a warm, moist environment that encourages yeast growth. Yeast thrives in warm and moist areas, particularly in the genital region.
6. Poor Hygiene Practices
While good hygiene is important, over-washing the vagina or using harsh soaps and douching can disrupt the natural balance of the vaginal flora, increasing the risk of a yeast infection. The vagina is self-cleaning, and it is best to avoid using scented products or chemicals that could irritate the area.
Symptoms of a Vaginal Yeast Infection
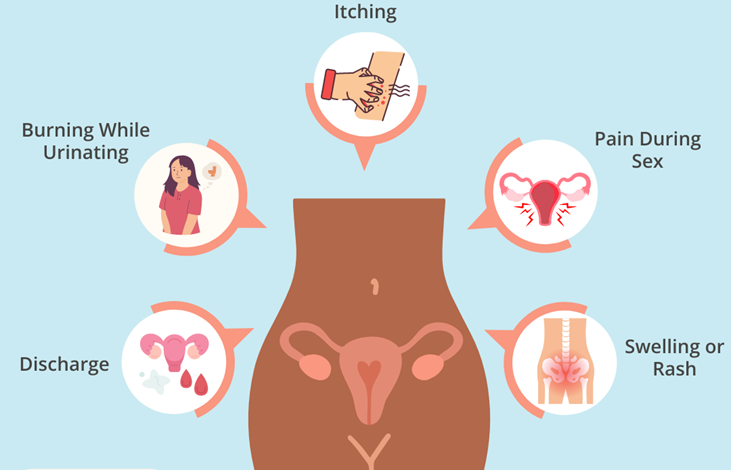
A vaginal yeast infection typically causes a range of symptoms, including:
- Itching or irritation: This is the most common symptom, with itching usually being localized around the vaginal opening.
- Thick, white discharge: The discharge often has a cottage cheese-like texture and may not have a strong odor.
- Burning sensation: This can occur during urination or sexual intercourse.
- Redness and swelling: The vaginal area may appear inflamed, with possible swelling of the vulva.
- Pain during sex: Some women experience discomfort or pain during intercourse.
It’s important to note that not all vaginal itching or discharge is due to a yeast infection. Other infections or conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can have similar symptoms. A healthcare provider can diagnose the condition and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Yeast Infections
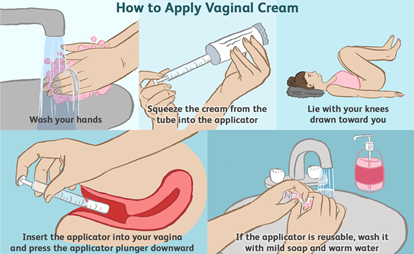
Vaginal yeast infections are typically treated with antifungal medications, which can be found in various forms, including creams, suppositories, and oral tablets. Some common treatment options include:
1.Over-the-counter (OTC) Antifungal Treatments
Many effective antifungal treatments are available over the counter at pharmacies. These include creams or suppositories that are applied inside the vagina or taken orally. Some of the most common OTC antifungal medications include miconazole (Monistat) and clotrimazole (Lotrimin).
2. Prescription Medications
For more severe or recurring yeast infections, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antifungal medications like fluconazole (Diflucan). In some cases, a longer course of treatment may be required.
3. Home Remedies (Caution Advised)
Some women turn to home remedies, such as using probiotics, coconut oil, or garlic, to help treat yeast infections. While there is limited scientific evidence to support their effectiveness, some individuals find these remedies helpful. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before trying these alternatives, as some can potentially cause irritation or worsen the infection.
Preventing Vaginal Yeast Infections

While yeast infections cannot always be avoided, certain lifestyle practices can help reduce the risk:
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash the vaginal area with warm water and mild soap, but avoid douching or using scented products that can cause irritation.
- Wear breathable underwear: Choose cotton underwear and avoid tight clothing that traps moisture and warmth.
- Practice safe sex: Although yeast infections are not considered sexually transmitted, sexual activity can trigger or worsen an existing infection. Using condoms can reduce the risk.
- Control blood sugar levels: For women with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels can help reduce the risk of yeast infections.
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics: Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare provider and avoid overuse.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Vaginal yeast infection (Candidiasis) . Retrieved from Mayo Clinic
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2022). Fungal infections and vaginal candidiasis . Retrieved from CDC.gov
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2021). Vaginal Candidiasis (Yeast Infection) . Retrieved from NIDDK.nih.gov
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Fungal infections: Vaginal Candidiasis . Retrieved from WHO.int