What is Food Poisoning?
Food poisoning occurs when you consume contaminated food or beverages. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or chemical substances.
Common Causes
- Bacterial Contamination
- Salmonella: Often found in undercooked poultry and eggs.
- E. coli: Associated with undercooked beef and contaminated produce.
- Listeria: Can be found in deli meats and unpasteurized dairy products.
2. Viral Infections
- Norovirus: Highly contagious and commonly spread through contaminated food or surfaces.
3. Parasites
- Giardia: Typically transmitted through contaminated water.
4. Chemical Contaminants
- Pesticides, heavy metals, and food additives can also lead to food poisoning.
Symptoms to Watch For

Symptoms can vary based on the source of contamination but often include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Fever
Most symptoms appear within hours or days after eating contaminated food.
How to Prevent Food Poisoning
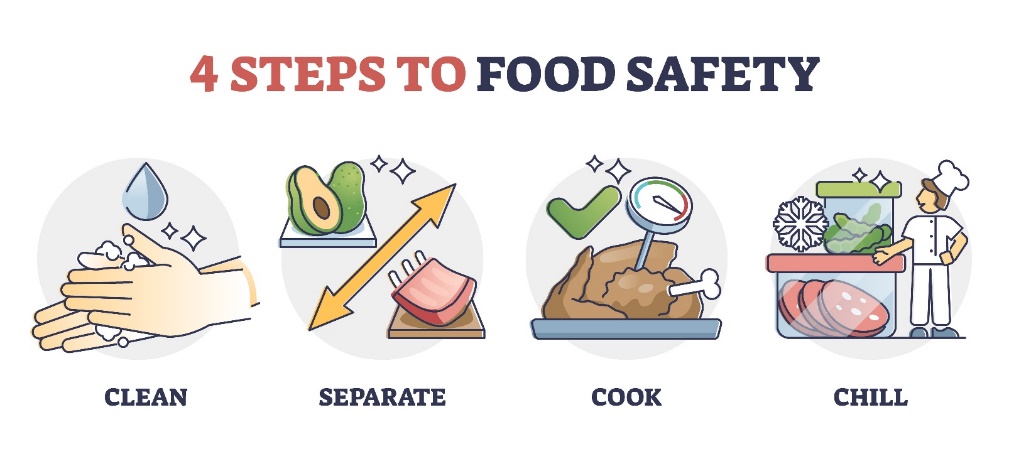
- Practice Safe Food Handling
- Always wash hands before preparing or eating food.
- Keep raw meat separate from other foods to avoid cross-contamination.
2. Cook Food Thoroughly
- Use a food thermometer to ensure meats reach safe internal temperatures.
3. Store Food Properly
- Refrigerate perishables promptly and keep your fridge at the correct temperature.
4. Be Cautious When Dining Out
- Choose reputable restaurants and ensure food is cooked fresh.
What to Do If You Suspect Food Poisoning
Experiencing symptoms that may indicate food poisoning can be distressing. Here’s a clear guide on how to manage the situation effectively:
1. Stay Hydrated

- Importance of Hydration
Dehydration is a common risk due to vomiting and diarrhea. Maintaining fluid intake is essential to support recovery. - Hydration Tips:
- Water: Drink small sips of water throughout the day to replenish fluids.
- Oral Rehydration Solutions: Consider electrolyte solutions, which can help replace lost minerals and fluids.
- Avoid Certain Beverages: Stay away from caffeine, alcohol, and sugary drinks, as they can irritate your stomach.
2. Probiotics

- Incorporating probiotics into your diet during recovery from food poisoning can support gut health, alleviate symptoms, and help restore balance to your microbiome. Whether through fermented foods such as yogurt or probiotics supplements, probiotics may play a valuable role in your overall recovery strategy.
3. Rest Your Body

- Why Rest Matters
Your body needs energy to combat the infection, making rest crucial for recovery. - Resting Suggestions
- Limit Activity: Refrain from strenuous tasks until you feel better.
- Create a Cozy Space: Find a comfortable area to relax, ideally away from noise and distractions.
4. Monitor Your Symptoms
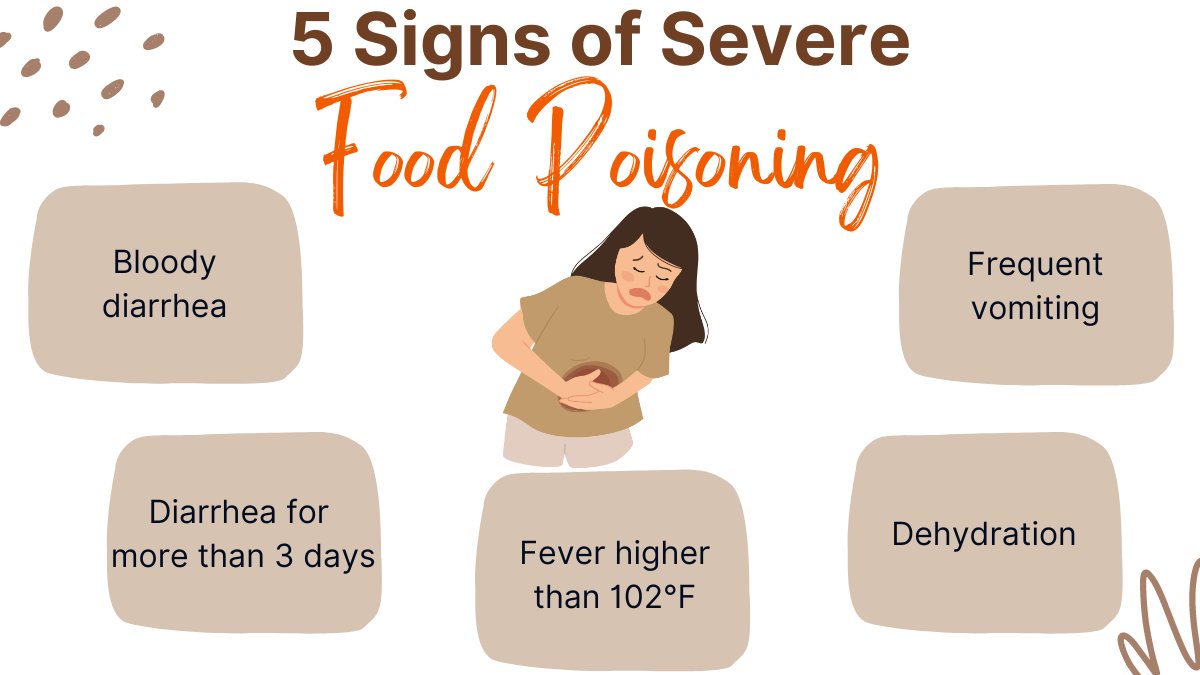
- Keep an Eye on Changes
Tracking your symptoms is essential to assess whether they are improving or worsening. - Symptoms to Watch For
- Severe abdominal cramps
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C)
- Ongoing vomiting
- Signs of dehydration like dizziness or dry mouth
5. Seek Medical Help If Necessary

- When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
If symptoms become severe or if you belong to a vulnerable group (young children, elderly, or those with compromised immune systems), it’s important to reach out to a healthcare professional. - Possible Medical Response
Treatment may include medications to control nausea or intravenous fluids for dehydration.
6. Report the Incident

- Importance of Reporting
If you suspect food poisoning from a restaurant or a specific food product, report it to local health authorities. This helps prevent further outbreaks and ensures food safety.
7. Gradually Reintroduce Food
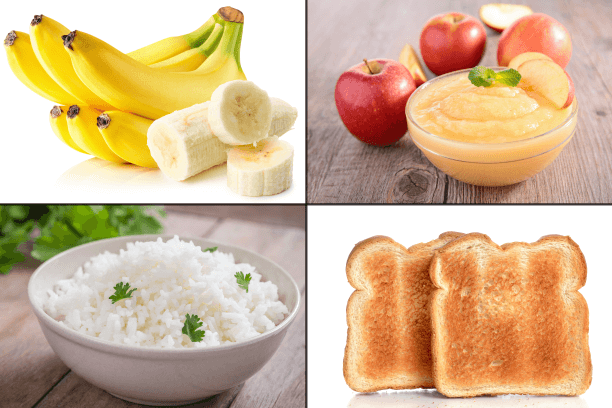
- Resuming Eating Slowly
Once symptoms begin to improve, reintroduce foods gradually, starting with bland options. - Gentle Foods to Start With
- Plain toast
- Rice
- Bananas
- Apple sauce
Avoid rice, spicy, or heavy foods until you're fully recovered.