What Is Influenza?
Influenza is caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs. These viruses are classified into three main types: A, B, and C. Types A and B are the most common in seasonal flu outbreaks, with Type A causing the most severe epidemics.
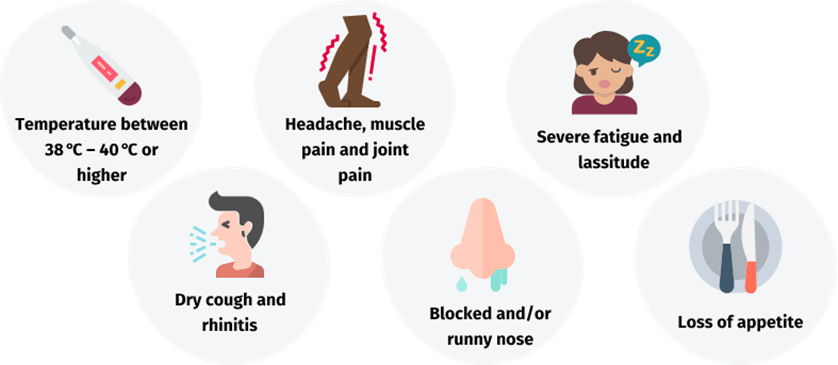
Symptoms of influenza typically include:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Runny or stuffy nose
In severe cases, influenza can lead to complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus infections, and worsening of chronic medical conditions like asthma and diabetes.
Prevention of Influenza

Preventing the flu is crucial, especially for those at higher risk, such as young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Here are key prevention strategies:
- Annual Flu Vaccination: The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent influenza. It is recommended for everyone over six months of age, especially individuals at higher risk of complications. While the vaccine may not always prevent infection, it can reduce the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications.
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), flu vaccines are updated annually to target the most common circulating strains.
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands with soap and water or using hand sanitizer can reduce the spread of the flu virus.
- Respiratory Etiquette: Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing with a tissue or elbow helps prevent the spread of respiratory droplets.
- Social Distancing: Staying home when sick and avoiding close contact with others helps reduce transmission, especially in crowded environments.
Treatment Options
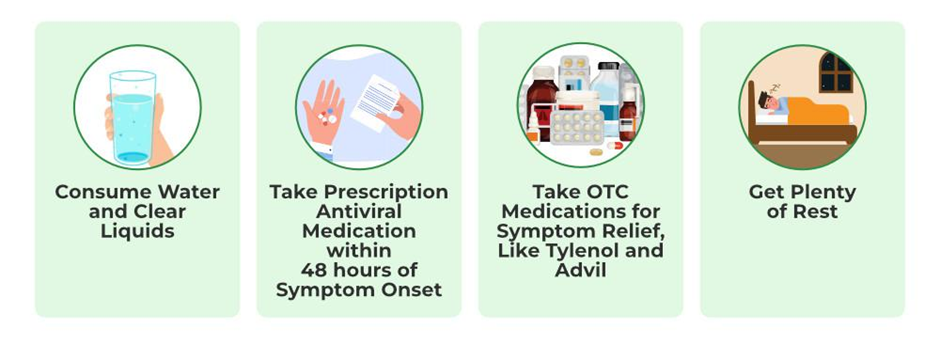
If someone contracts the flu, there are several treatment options that can reduce the severity and duration of illness. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu), zanamivir (Relenza), and baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza), are commonly prescribed to shorten the duration of symptoms if taken early in the course of infection.
- Antiviral Medications: These medications are most effective when started within the first 48 hours of symptom onset. They work by inhibiting the replication of the flu virus.
- Symptomatic Relief: Over-the-counter (OTC) medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) can help reduce fever and alleviate muscle aches. Decongestants, cough syrups, and saline nasal sprays may help relieve symptoms.
- Rest and Hydration: Staying hydrated and getting ample rest is essential for recovery.
Role of Pharmacists in Flu Management
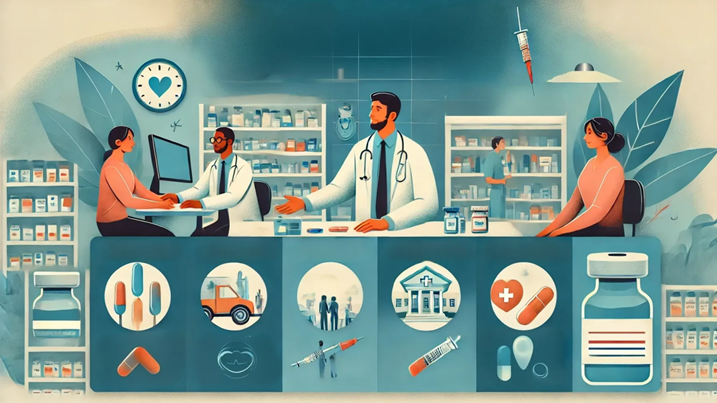

Pharmacists play an essential role in flu management, both in prevention and treatment:
- Flu Vaccination Clinics: Many pharmacies offer convenient flu vaccination services, providing easy access for patients who may not be able to visit a doctor. Pharmacists are trained to administer vaccines and can provide valuable information about the vaccine's effectiveness and safety.
- Antiviral Prescriptions: Pharmacists can counsel patients on antiviral medications, ensuring they are used appropriately. Some pharmacies also have the ability to prescribe antiviral treatments, depending on local regulations.
- Symptom Management: Pharmacists can guide patients on the proper use of OTC medications and recommend other remedies for symptom relief, providing expert advice on managing flu-related discomfort.
- Education: Pharmacists can educate patients on the importance of preventive measures like handwashing, vaccination, and avoiding the spread of germs, which are essential for community health.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2023). Influenza (Flu). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/flu/index.htm
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Influenza. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal)
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Influenza Antiviral Medications. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/
- Immunization Action Coalition. (2023). The Importance of Flu Vaccination. Retrieved from https://www.immunize.org/